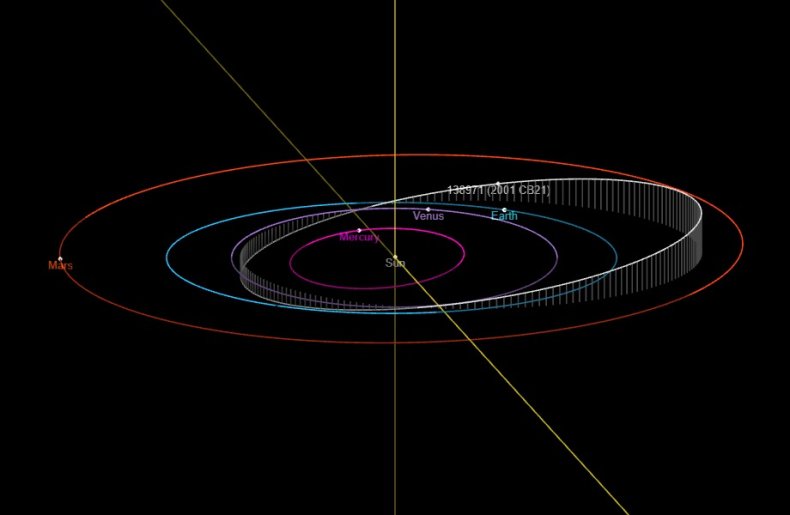
An asteroid that might have a diameter as nice as 4265 ft is headed in the direction of a detailed strategy to Earth on March 4. Although asteroid (138971) 2001 CB21 will safely miss our planet, that does not imply skywatchers will miss out.
The Digital Telescope Mission 2.0 is giving house lovers the chance to look at (138971) 2001 CB21 because it passes Earth at a distance of round 3 million miles safely from the consolation of their very own house.
Although this will look like a terrific distance, it's shut sufficient for NASA to categorise it as a Close to-Earth Asteroid. It is usually massive sufficient to be labeled as a Probably Hazardous Object, despite the fact that there's little probability of it hitting Earth within the subsequent 100 years.
The stay feed from the telescope will start at 10 pm ET (03:00 UTC) on March 4, 2022, on Digital Telescope's WEBTV channel.
For anybody who needs to see the item's strategy to Earth, the asteroid might be tracked nearly at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Small-Physique Database Lookup web site. Utilizing the simulator it's attainable to wind the orbit of (138971) 2001 CB21 to see when it should cross paths with Earth.
In keeping with NASA's Middle for Close to-Earth Object Research (CNEOS), when (138971) 2001 CB21 makes its shut strategy to Earth it is going to be touring at about 7.5 miles per second.
That's about 13 instances sooner than a bullet fired by an M16 rifle or 18 instances sooner than the utmost pace of a Lockheed Martin F-16 jet fighter.
CNEOS has calculated the orbit of (138971) 2001 CB21 for the century at the least, and whereas it takes simply 384 days (1.05 years) to orbit the solar, it will not come this near earth once more for a while.
The subsequent time(138971) 2001 CB21 makes a detailed strategy to Earth inside round 3 million miles might be March 6, 2043, when it should come inside 2.99 million miles of our planet.
CNEOS estimates a diameter for (138971) 2001 CB21 of between 1837 and 4265 ft. The explanation for this disparity is all the way down to how astronomers estimate the sizes of those house rocks.
How Do NASA Estimate Asteroid Sizes?
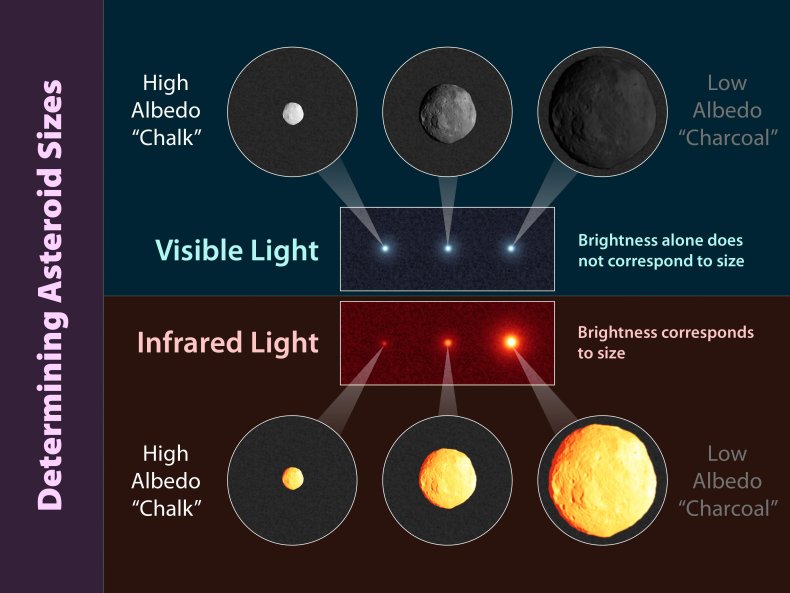
To find out the diameters of asteroids, astronomers measure the seen gentle from the solar mirrored off its floor, a measure often known as albedo.
Dimension is not the one figuring out think about how a lot gentle an asteroid displays, nevertheless. It may additionally rely upon the fabric from which the asteroid consists and the way unfastened or tightly packed that materials is on the object's floor
Albedo additionally will depend on the colour of the asteroid, so a lighter "chalky" asteroid that has looser or dusty materials at its floor will seem deceptively massive to astronomers, whereas an asteroid with a charcoal-like floor will replicate much less gentle, thus showing smaller than it really is.
So, from hundreds of thousands of miles away, a big and darkish asteroid may look like the identical measurement as a smaller, lighter coloured one.
One other method of estimating an asteroid's measurement includes measuring the quantity of warmth it offers off because it travels by house by observing it in infrared gentle.
This could possibly be a greater indicator of measurement than mirrored seen gentle, as a bigger object would seem brighter in infrared gentle, unaffected by the quantity of seen gentle it displays.
In keeping with NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on the California Institute of Expertise, which operates CNEOS, one of the best ways to find out asteroid measurement is a mix of observing the visible gentle it displays and measuring its infrared signature.


Post a Comment