The World Meteorological Group (WMO) has recorded two new world information for megaflashes of lightning which occurred in hotspots for such exercise in North and South America.
Megaflash lightning is outlined as discharges that cowl a horizontal distance of a whole bunch of miles, typically lasting a number of seconds. Megaflashes don't happen in abnormal thunderstorms. They require expansive electrified clouds that discharge at sufficiently low charges to facilitate single horizontal flashes spanning extraordinary distances.
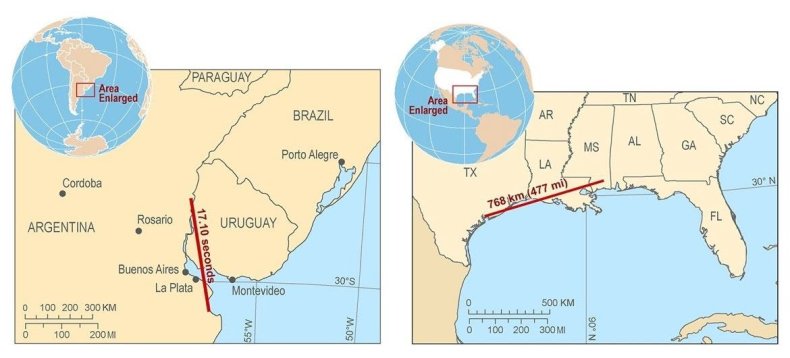
The longest single flash coated a horizontal distance of round 477.2 miles, inside a margin of error of 5 miles. The flash prolonged between Texas and Mississippi, protecting the width of Louisiana. The megaflash was over one and a half occasions the size of the Grand Canyon or the identical as the gap between New York and Columbus, Ohio.
The space file was measured in elements of the southern United States on April 29, 2020 and beats the earlier file, set in Brazil throughout 2018, by round 37 miles.
The second file concerned occasions fairly distances with the WMO recording a single lightning flash that lasted over 17.1 seconds. The length file was set by a flash that developed in a thunderstorm over Uruguay and northern Argentina on June 18, 2020.
That is longer than the earlier biggest length lightning flash by simply over a 3rd of a second (0.37 seconds), which developed over Argentina in 2019.
Professor Randall Cerveny was appointed by WMO's Climate and Local weather Extremes to report their findings. He stated in a press launch: "These are extraordinary information from single lightning flash occasions. Environmental extremes live measurements of the facility of nature, in addition to scientific progress in with the ability to make such assessments.
"It's seemingly that even larger extremes nonetheless exist, and that we can observe them as lightning detection know-how improves."
The flashes have been documented in a paper revealed within the American Geophysical Union's journal Geophysical Analysis Lettersforward of Worldwide Lightning Security Day on June 28.
The power to measure more and more massive megaflashes is the results of the WMO using space-based lightning mapping know-how like Geostationary Lightning Mappers on the R-series Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES-16 and 17) which made these record-breaking measurements.
Not solely do these space-based platforms enhance on beforehand used ground-based Lightning Mapping Array networks, which established earlier information, however they need to additionally present near-global protection of whole lightning. This consists of monitoring hotspots in South and North America just like the La Plata basin and the Nice Plains.
WMO Secretary-Common Professor Petteri Taalas emphasised the significance of higher understanding megaflashes. He stated: "Lightning is a serious hazard that claims many lives yearly. The findings spotlight vital public lightning security issues for electrified clouds the place flashes can journey extraordinarily massive distances."


Post a Comment