German researchers have found that paralyzed stroke sufferers might get better vital mobility after receiving an electrical present to their brains.
Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Mind Sciences in Leipzig, the College Medical Middle Halle and the Charite-Universitaetsmedizinin Germany's capital, Berlin, revealed that such noninvasive mind stimulation might considerably enhance sufferers' impaired motion.
The remedy confirmed notable results after a single utility and might be individually adjusted for various sufferers for his or her optimum profit, in keeping with the researchers, who printed their findings within the journal Mind Stimulation.
Analysis group chief Bernhard Sehm revealed that arm paralysis, which happens resulting from physiological and structural post-stroke mind modifications, is likely one of the most frequent penalties of mind harm.
"The premise of those modifications are each reparative mind processes and behavioral patterns of on a regular basis actions after the stroke," stated Sehm, a senior doctor on the College Clinic and Polyclinic for Neurology on the College Medical Middle Halle.
"With the assistance of transcranial direct present stimulation (tDCS), one can affect these modifications within the mind. The currents penetrate the mind tissue, the place they've an area excitatory or inhibitory impact."
The research included 24 sufferers with "very restricted" mobility resulting from stroke.
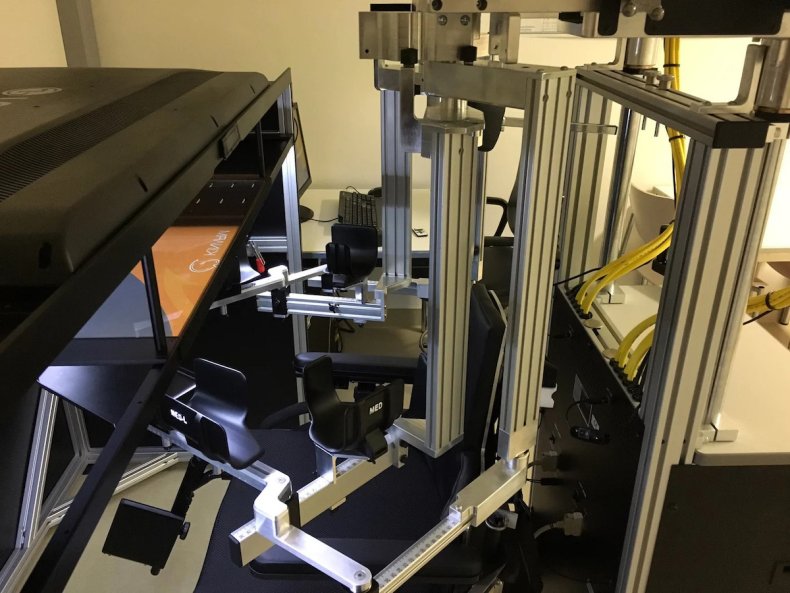
"Within the lab, we've a robotic system that may be individually tailored to every affected person — a form of exoskeleton that allows them to maneuver their paralyzed arm and carry out duties in a digital surroundings," stated lead creator Toni Muffel of the Charite-Universitaetsmedizin college hospital in Berlin.
Muffel stated the sufferers' scalps have been stimulated by way of electrodes whereas they interacted with the digital objects. "In parallel, we measured how effectively, or how poorly, the mind stimulation helped the members to carry out the duties," he stated.
Sehm stated that mind stimulation had a noteworthy impact on the mind areas affected by the stroke.
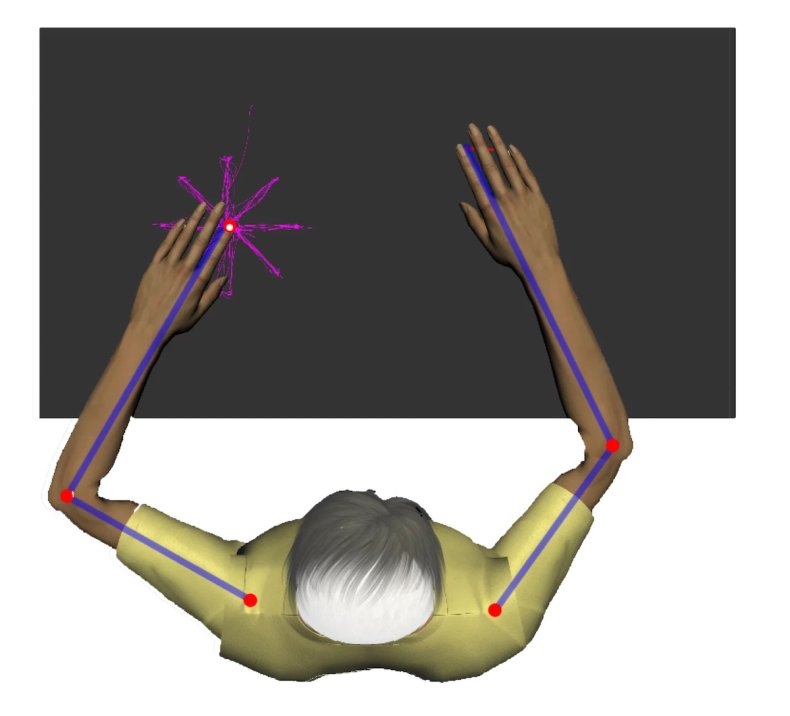
"Our robotic system permits us to measure numerous motor capabilities concurrently and thus acquire a complete image of the stimulation results. The information present that sensorimotor capabilities of the paralyzed arm are clearly influenced by tDCS," Sehm stated.
"Nevertheless, we couldn't establish a uniform helpful sample throughout completely different sufferers. As an alternative, the modifications within the mind areas diversified relying on the duty and the electrode placement," he stated.
"Which means sooner or later, sufferers will must be carefully examined earlier than mind stimulation therapy in an effort to develop a focused and individualized method to their deficits. This easy however promising technique of mind stimulation will then have a future in affected person care."

This story was offered to Newsweek by Zenger Information.

Post a Comment